Medication After Hair Transplant For Optimal Healing
Did you know the success rate of hair transplant is 97% which is only achieved through proper post-operative care? Most patients focus on the hair transplant procedure itself. However, adopting habits like avoiding smoking and direct sunlight, and using medications after hair transplant delivers long-term benefits.
These medications strengthen hair, improve hair growth, and preserve the transplanted hair follicles. However, you need to know the right approach to use medications for a successful transplant.
In this article, we’ll reveal which medications are recommended after hair transplant surgery, why they are beneficial, and when to use them. You’ll also find a detailed post-op medication timeline and tips for managing side effects and long-term care.
Why Medication Matters After Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure performed for hair restoration in areas of the scalp affected by pattern hair loss or thinning. For a successful surgery, surgeons recommend taking certain medicines before, after, and during the procedure.
Post-hair transplant medications help prevent pain and swelling and ensure optimal healing.
- Local anesthetics are used during surgery for a painless procedure.
- Cortisone is applied after surgery to prevent inflammation.
- A few medicines are prescribed to boost the healing process and recovery time.
- Surgeons also recommend medications for fast and healthy hair growth.
What Medications Should I Take After Hair Transplant?
The most common prescription medications after hair transplant include:

Antibiotics
Antibiotics defend against bacterial infections after surgery. Bacteria can reside in the scalp in ultra-small sites that disrupt the healing process and cause infections.
Scalp itching, redness, and swelling are the major signs of post-transplant infections. It can also cause loss of hair patches from the transplanted region.
The best antibiotics after a hair transplant include:
- Amoxicillin
- Ciprofloxacin
- Cephalexin
These antibiotics do not directly affect hair loss or surgery, but they fight bacteria to eliminate the risk of infections.
NSAIDs/Corticosteroids
Incisions made during surgery may cause inflammation and swelling around the eyes and forehead. Anti-inflammatory drugs control swelling and prevent further inflammation.
Doctors prescribe post-hair transplant medications like Prednol, Diclofenac, or Naproxen to stop the accumulation of fluid in the affected areas. It helps reduce inflammation during recovery and relieves pain.
Antihistamines
The implanted hair grafts may feel itchy and scratching can worsen the condition of transplanted hair follicles. This is why doctors prescribe antihistamines, e.g., Cetirizine, Zyrtec, and Benadryl, to use only when a patient feels intense irritation. These medications prevent itchy scalp and smooth the healing process.
In addition, scalp treatments containing steroids, saline sprays, and particular shampoos are used, which hydrate the surgical area and ease the discomfort.
Heart, thyroid, blood pressure, and asthma patients should avoid using these medications after hair transplant.
Pain Killers
Doctors advise patients to take painkillers after hair transplant surgery to alleviate the post-surgery pain. Patients feel this discomfort after the effects of anesthetics used during surgery wear off.
You can take painkillers like Paracetamol and Ibuprofen for 3-5 days to relieve pain. Avoid using alcohol while taking these medications because it may cause dizziness and lead to serious complications.
See Also: How To Protect Hair From Sun
What Topical Ointments Are Used After Hair Transplant?
The topical ointments highly recommended by hair transplant surgeons include:

Minoxidil (Rogaine)
Minoxidil is a liquid or foamy topical medication known by its brand name Rogaine. Many dermatologists recommend minoxidil for hair regrowth after transplantation.
- It minimizes hair shedding after the transplant.
- It prevents the loss of original hair.
- It improves blood flow to the new hair grafts.
- It prolongs the anagen phase of the hair growth cycle by dilating blood vessels around hair follicles.
- It also reactivates dormant hair follicles and promotes new hair growth.
Finasteride
Propecia contains hair growth drug finasteride, which is used for treatment of male pattern hair loss. It comes in both oral and topical forms and helps boost hair regrowth when used.
- Finasteride blocks the production of DHT in the body, a hormone responsible for hair thinning and pattern baldness.
- It also protects the transplanted hair grafts and actual hair of the patient.
Patients are advised to use minoxidil and finasteride consistently for 3-4 months to see the desired outcomes.
However, Finasteride is generally not recommended for females due to potential side effects such as:
- Birth defects (especially in male fetuses)
- Changes in mood (anxiety & depression)
- Decreased libido
- Irregular menstrual periods
- Dizziness
- Breast tenderness
PRP Therapy
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a non-surgical therapeutic technique for improving hair health after surgery. It injects the platelets taken from the patient’s own blood into the affected areas of the scalp.
This is done to ensure smooth blood circulation in the hair follicles and repair the damaged tissues. This therapy has no intense side effects or allergic reactions and can be applied before and after hair transplant.
Biotin & Supplements
Biotin (Vitamin B7) and other vitamins, including vitamins A, C, D, and E, help with quick recovery and boost growth after a hair transplant.
Moreover, minerals like iron and zinc are also helpful in the production of keratin and in strengthening hair follicles. However, patients should consult their surgeon before taking these supplements.
See Also: Can Too Much Vitamin A Cause Hair Loss
Coraspin After Hair Transplant-Necessary Or Not?
Aspirin (Coraspin) can thin the blood and, in turn, help regulate blood flow in the hair follicles and improve healing. It also minimizes the formation of blood clots and preserves the transplanted hair patches.
However, it can stimulate bleeding after a hair transplant. This is why, Coraspin shouldn’t be taken within 3 days after surgery.
When To Start Medication After Hair Transplant?
Post-hair transplant medications should be started shortly after surgery. Using each medication at the right time is necessary for better recovery and successful results.
| Time Period | Medication | Purpose |
| Day 0-5 | Antihistamines, Painkillers (anti-aspirin) | Prevent itching and pain |
| Day 0-7 | Antibiotics, Corticosteroids | Fight infections, reduce swelling |
| Day 3-7 | Coraspin | Improve healing and blood flow |
| Day 8-30 | Minoxidil, Finasteride, Biotin | Stimulate hair regrowth |
| After 6 Months | PRP Therapy, Derma Rollers, & Other supplements | Support transplanted hair and healing |
How Long to Take Medication After Hair Transplant?

Post-hair transplant medications should be taken as advised by your surgeon. Antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are usually taken for a short interval, while hair growth stimulants, e.g., minoxidil and finasteride, are used for a long time for desired results.
Some surgeons recommend specific medications for lifelong intervals. A surgeon calls it a lifetime commitment to take medications after hair transplant:
“All these medications are lifetime commitments; if you stop them, whatever you gain/maintain will be gone about 6 months later.”
Medication After FUT vs. FUE Hair Transplant
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) involves extracting small hair patches from the back or sides of the scalp. On the other hand, in Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT), a strip containing hair tissues is transplanted to the affected region, which is often recommended for larger areas of baldness.
Doctors recommend using the same types of medications after hair transplant for both patients. However, the duration and extent of medication depend on the severity of the procedure and patient-specific conditions.
Hair growth stimulants, including minoxidil, finasteride, biotin, and other supplements, can be used after both FUT and FUE to improve scalp health. The actual difference is in the pain relievers and anti-inflammatories. Here is a quick overview of FUT and FUE:
| Features | FUT | FUE |
| Procedure Time | Faster for a large number of transplantations | Slow due to smaller incisions |
| Pain & Discomfort | Very painful | Less painful than FUT |
| Scarring | Large linear scar in the donor area | Tiny, negligible scars |
| Recovery | Longer recovery with discomfort and tightness | Quick recovery with minimal discomfort |
| Medications | Analgesic painkillers, anti-anxiety medications and high potency antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs | Paracetamol and Ibuprofen for pain, antihistamines, and Keflex or Cephalexin antibiotic |
What Happens if You Stop Medication after Hair Transplant?

The implanted hair follicles resist balding and grow consistently after hair transplants. But medications are needed to prevent hair loss and infections. If you stop taking medicines:
- Hair loss will occur in non-transplanted regions.
- You may experience male or female pattern hair loss.
- You may observe thinning in your scalp due to slow blood circulation.
- The benefits to your existing hair may diminish.
What To Avoid During Recovery: Medications & Habits

Hair transplant requires proper care and healing time for a healthy scalp. Must adopt these habits right after your hair transplant surgery:
- Keep your hair and scalp clean.
- Keep yourself hydrated and eat a nutritious diet.
- Limit direct sun exposure to protect your scalp from burning.
- Do not use alcohol or smoke during the healing process .
- Avoid heavy lifting and difficult exercises.
- Avoid scratching when you feel itchiness.
- Take medications prescribed by your doctor.
See Also: Sex After Hair Transplant
When Not to Use Medication After Hair Transplant?

The prescription medications after a hair transplant may have certain side effects. During consultations with your hair transplant surgeon, let them know if you have:
- A chronic disease.
- Diagnosed allergic reaction after a certain medication.
- Mental health disorder.
Some post-hair transplant medications have specific contraindications, and doctors recommend not to use them in particular health conditions. Some of which are:
- Antihistamines: High blood pressure, cardiac disease and asthma.
- Minoxidil: Eczema; heart, kidney, or liver disease.
- Liquid & Oral Steroids: Patients with mental health issues, blood pressure, epilepsy, stomach ulcer, diabetes, and liver problems.
Managing Hair Transplant Side Effects
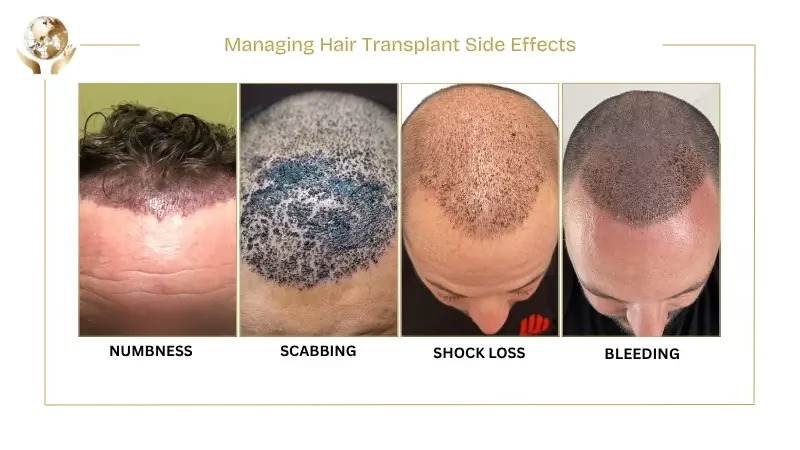
Hair transplants have minimal side effects like itching, swelling, or infections that can be handled with proper care and medication. Some adverse side effects are:
- Numbness: Any nerve disrupted during surgery may cause numbness in the scalp that resolves over time during recovery.
- Scabbing: You may notice scabs around the newly implanted hair grafts. Avoid touching and picking at these areas to prevent inflammation. They will heal naturally in 10-14 days.
- Shock Loss: The transplanted hair may enter a dormant phase, during which you’ll experience temporary hair loss. It is a part of the recovery process and hair will regrow after this phase.
- Bleeding: The donor and recipient areas of the scalp might suffer from bleeding, which should be looked after and followed by immediate consultation with the doctor.
How To Provide Long-Term Care After A Hair Transplant?

For lifelong results, you need to be patient with your hair transplant recovery for at least 12-18 months. Adopting a healthy lifestyle is necessary for minimizing side effects and preventing future complications:
- Gently wash your hair using lukewarm water and mild shampoos.
- Avoid harsh rinsing or scrubbing your scalp.
- Use vitamins, omega-3 fatty acids, and proteins in your diet.
- Protect your scalp from trauma or injury.
- Avoid tight hairstyles and harsh chemicals.
See Also: Is Hair Transplant Permanent

This article is medically reviewed by Medical Aesthetic Dr. Ali Khalil (PHD)
See Our Doctors & Surgeons
Can you get results from hair transplant without medication?
Yes, a successful hair transplant can be performed without medications for patients with a stable scalp and slow hair loss.
Does Costco have minoxidil?
You can buy topical minoxidil from Costco for both men and women.
Does minoxidil cause weight gain?
Yes, both oral and topical minoxidil cause weight gain as a side effect.
Is rosemary oil better than minoxidil?
While minoxidil is more effective for hair growth, rosemary oil is a natural alternative with fewer side effects and stimulates hair regrowth by blocking DHT.






